Megatron入门:张量并行
前言
Megatron 的核心思想是通过张量并行(Tensor Parallelism)与流水线并行(Pipeline Parallelism)相结合的方式,在 GPU 集群上实现超大规模语言模型的高效训练。
张量并行和流水线并行,同属于模型并行,简单地理解就是将模型参数按不同维度切分成小块,放到不同GPU上并行计算。
张量并行原理
张量并行属于模型并行的一种,旨在于将模型“纵向”切分成更小的“块”,放到不同GPU上进行并行计算。
理解模型的张量并行,需要从基础的矩阵乘法说起。
并行矩阵乘法
对于一个矩阵乘法$X @ W = Y$
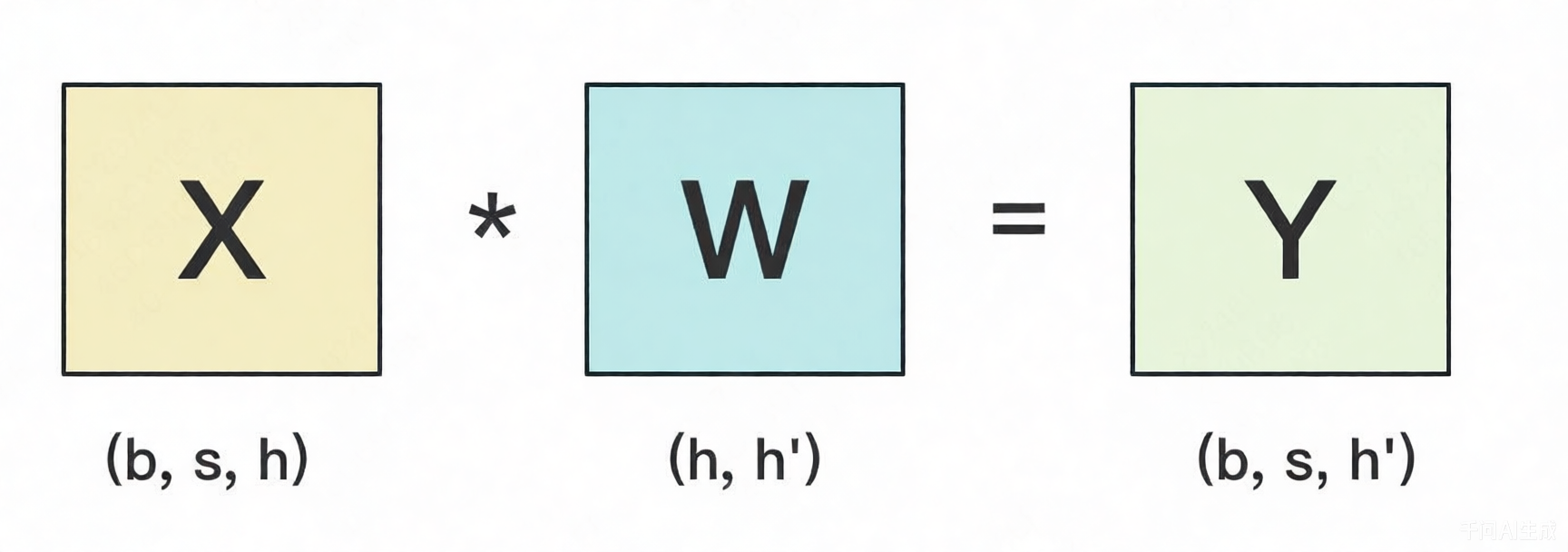
假设W很大,导致单卡装不下。我们需要把W切开放不到不同的卡上。显然我们可以沿着W的行维度,或者列维度进行切分。
按行切分
假设有N张GPU,就可以把权重W切成N份。下图展示N=2的切割方式。
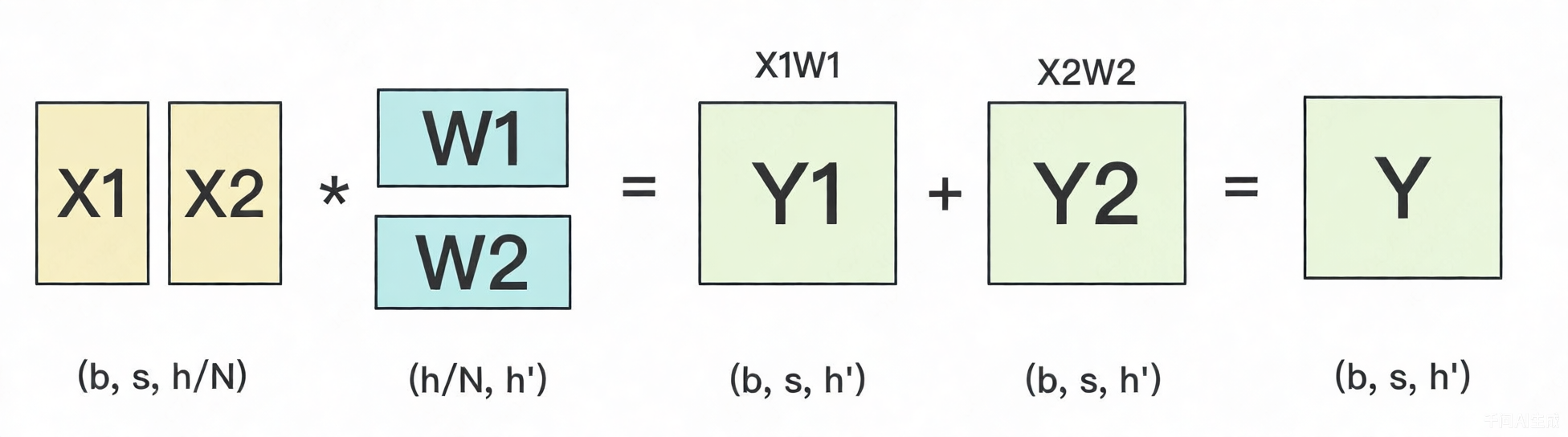
W按行切分,X就得按列对应切分。接着将按行切分展示成并行的方式。
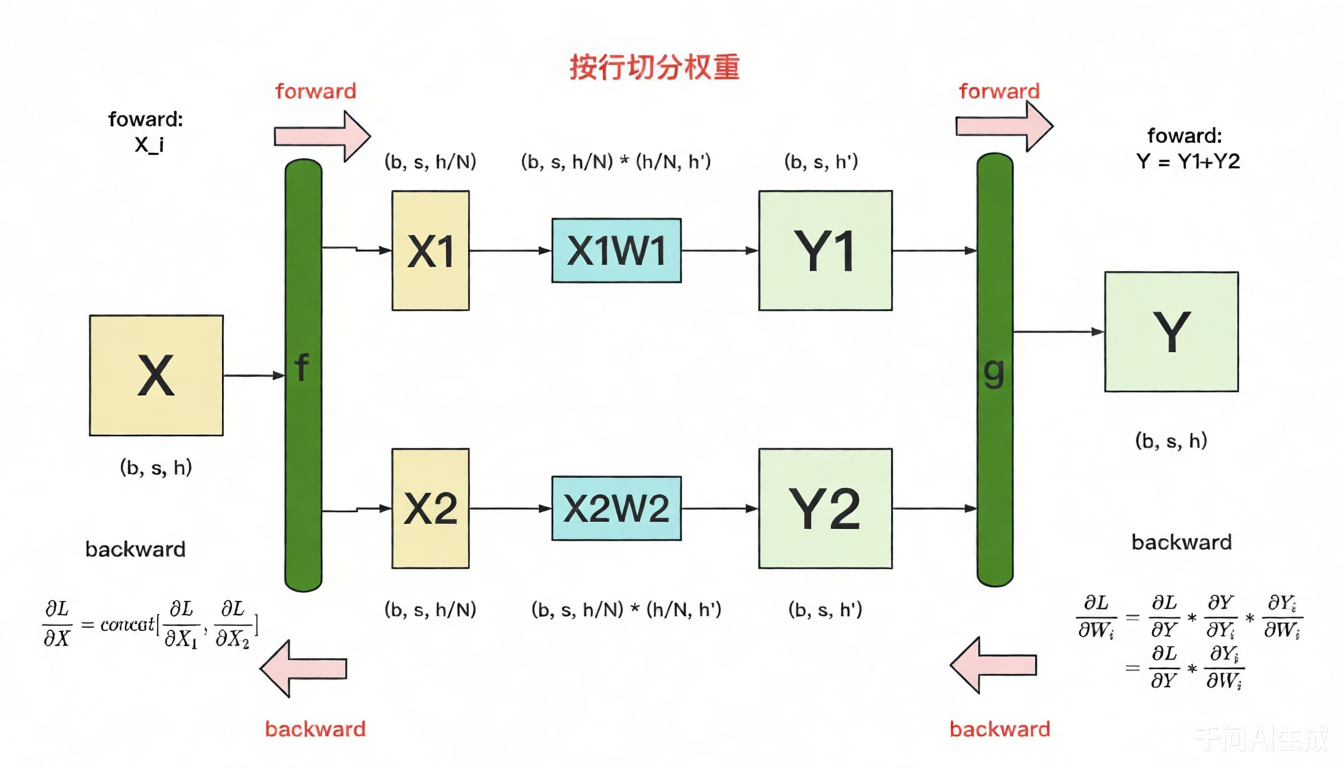 图中的每一行表示单独在一块GPU上的计算过程。
图中的每一行表示单独在一块GPU上的计算过程。
f和g分别表示两个算子,每个算子都包括一组forward和backward操作。f的forward是将X按列切分成两块,放到两个GPU上。相应的 backward是将两块GPU上的梯度$\frac{\partial L}{\partial X1}$和$\frac{\partial L}{\partial X2}$gather到一起。g的forward是将Y1和Y2相加得到Y,backward是将$\frac{\partial L}{\partial Y}$广播到各个GPU上。
按列切分
W也可以按列切分。
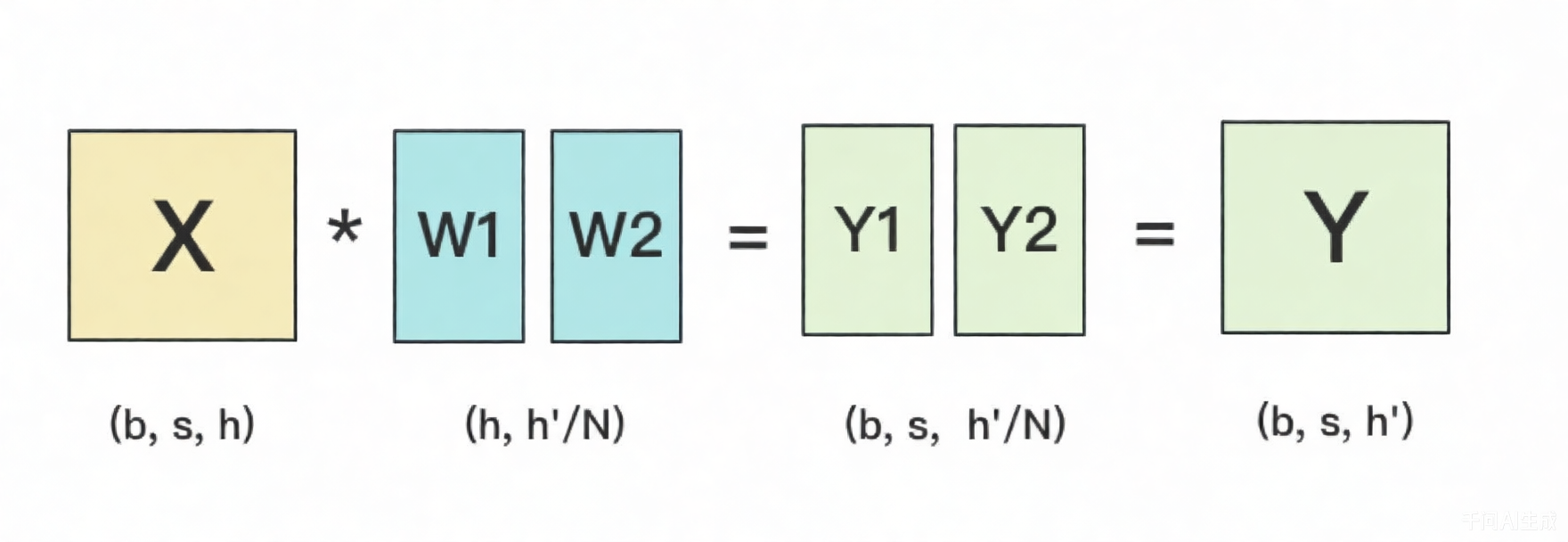
展示成并行的形式。
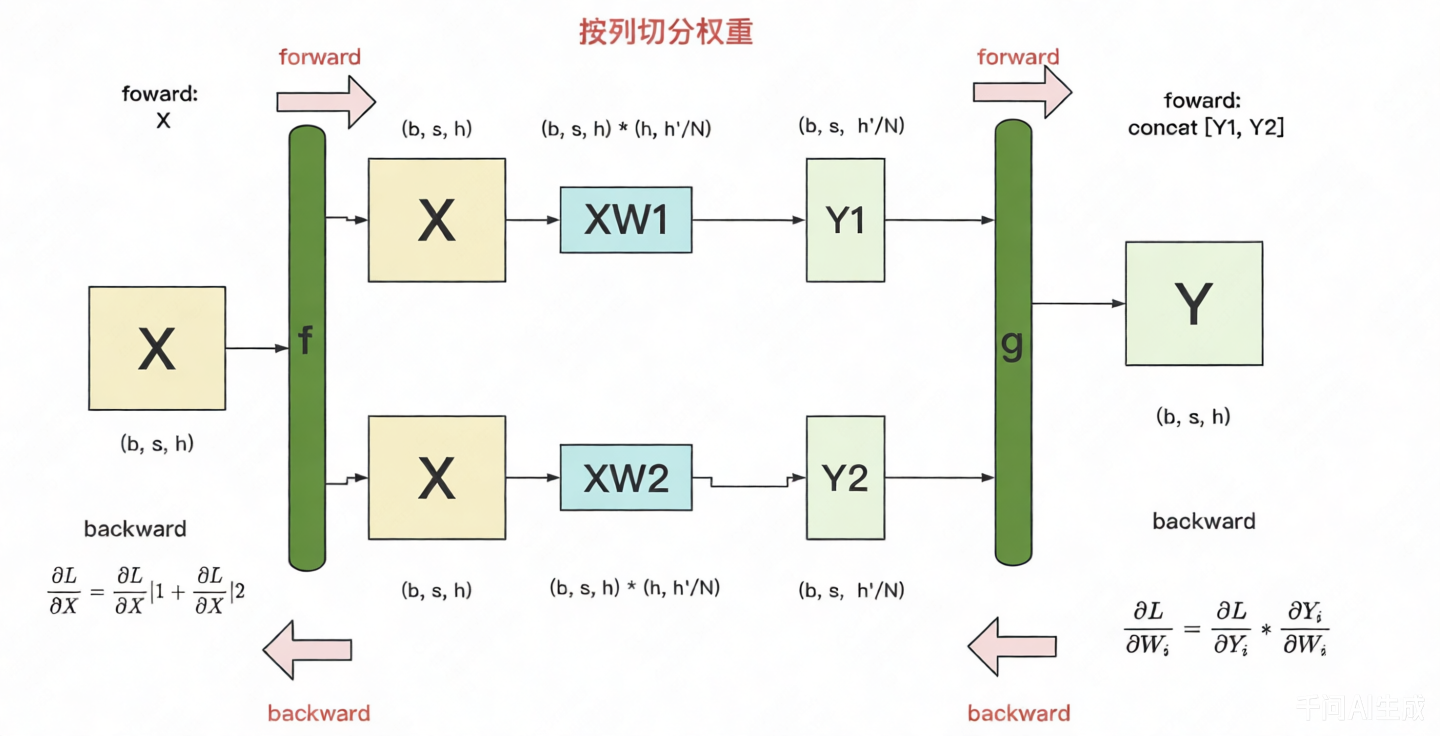
- 按列切分时,
f的foward时将X复制到各个GPU上,backward是将各个GPU上的梯度$\frac{\partial L}{\partial X}$AllReduce到一起; g的forward将Y1和Y2 gather到一起,backward是将$\frac{\partial L}{\partial Y}$切分到各个GPU上;
“按行”和“按列”切分权重的方法是Megatron-LM中的基础算子,MLP、Attention等权重的切分操作就是由这两个基础算子组合而成的。
MLP层张量并行
MLP的计算过程由两个矩阵乘法和非线性激活函数组成,示意图如下。
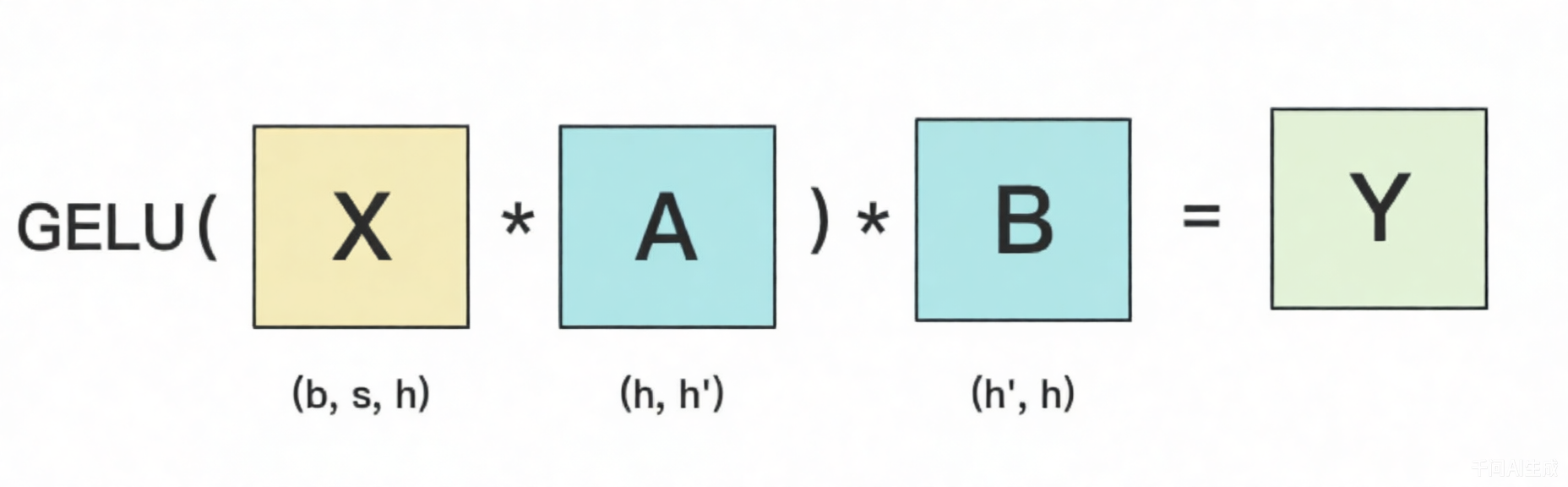
其中,GELU是激活函数,A和B分别为两个线性层的权重。在Transformer里,一般设h’ = 4h。假设现在有N块GPU,我们要把MLP层的权重拆到上面做计算,Megatron提供的拆分办法如下:
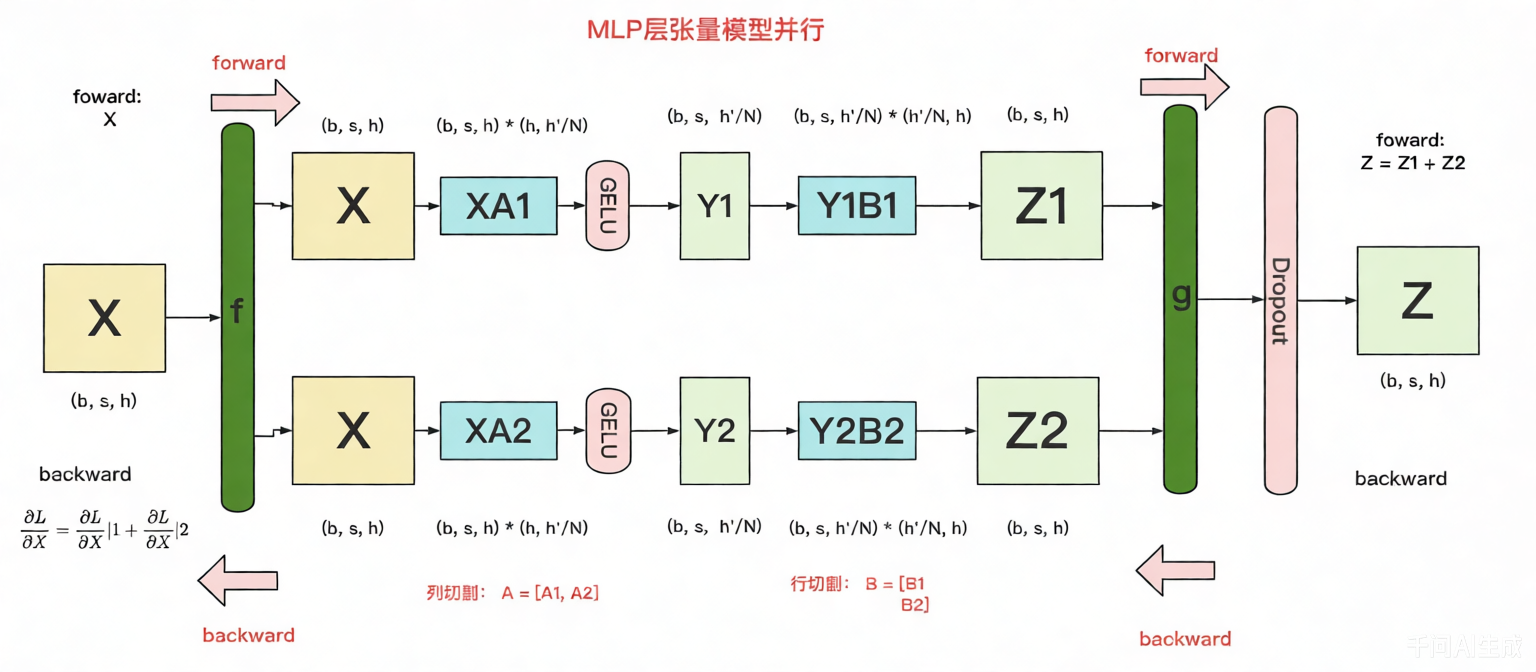
在MLP层中,对权重A采用“列切割”,对权重B采用“行切割”。
f的forward计算:把输入X拷贝到两块GPU上,每块GPU即可独立做forward计算。g的forward计算:每块GPU上的forward的计算完毕,取得Z1和Z2后,GPU间做一次AllReduce,相加结果产生Z。g的backward计算:只需要把梯度 $\frac{\partial L}{\partial Z}$拷贝到两块GPU上,两块GPU就能各自独立做梯度计算。f的backward计算:当前层的梯度计算完毕,需要传递到下一层继续做梯度计算,此时需要求得 $\frac{\partial L}{\partial X}$ ,然后两块GPU做一次AllReduce,把各自的梯度相加即可
先对A“列切割”然后对B“行切割”的原因是可以保证各GPU上的计算相互独立,减少通讯量。MLP层做forward时产生一次AllReduce,做backward时产生一次AllReduce。AllReduce的过程分为两个阶段,Reduce-Scatter和All-Gather,每个阶段的通讯量都相等。现在我们设每个阶段的通讯量为$\Phi$ ,则一次AllReduce产生的通讯量为$2\Phi$ ,MLP层的总通讯量为 $4\Phi$ 。
多头自注意力层
多头自注意力层包含每个头的SelfAttention计算,然后每个头的hidden向量concat后,再经过一个线性层。
其切分核心是将每个头的权重放到不同GPU上进行计算。
下图展示了当num_heads = 2时attention层的计算方法。
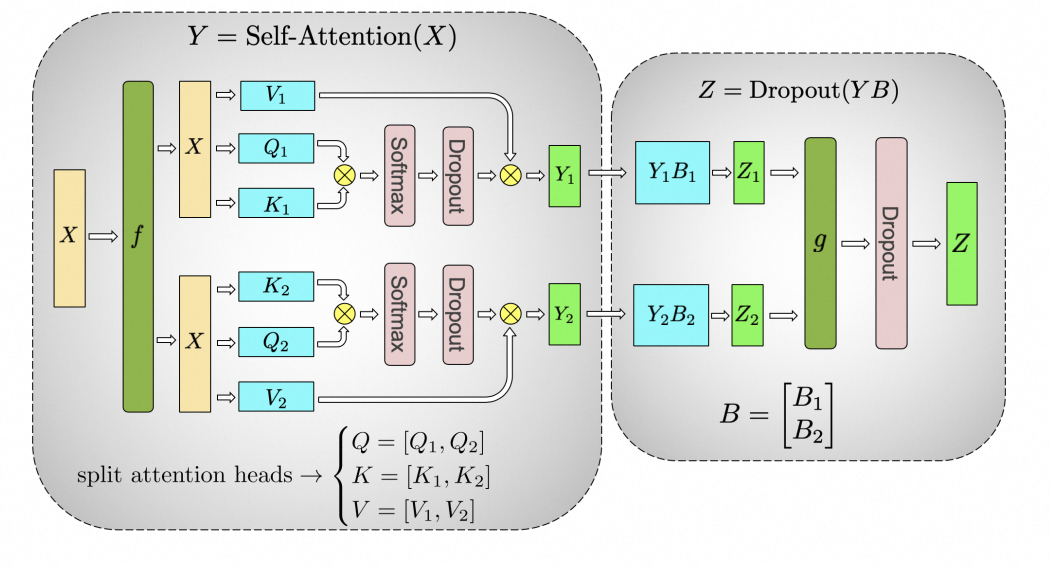
对三个参数矩阵Q,K,V,按照“列切割”,每个头放到一块GPU上,做并行计算。对线性层B,按照“行切割”。切割的方式和MLP层基本一致,其forward与backward原理也一致。
在实际应用中,并不一定按照一个head占用一块GPU来切割权重,我们也可以一个多个head占用一块GPU,这依然不会改变单块GPU上独立计算的目的。
类比于MLP层,self-attention层在forward中做一次AllReduce,在backward中做一次AllReduce。总通讯量也是$4\Phi$。
Embedding层
输入层和输出层,均存在embedding层。
Embedding层一般由两个部分组成:
- word embedding:维度(v, h),其中v表示词表大小。
- positional embedding:维度(max_s, h),其中max_s表示模型允许的最大序列长度。
通常positional embedding对显存压力不大,可以每个GPU上拷贝一份。但词表一般较大,因此需要把word embedding拆分到各个GPU上。
对于输入层embedding来说,将ebmedding矩阵按行切割,各自查表。具体的做法如下:
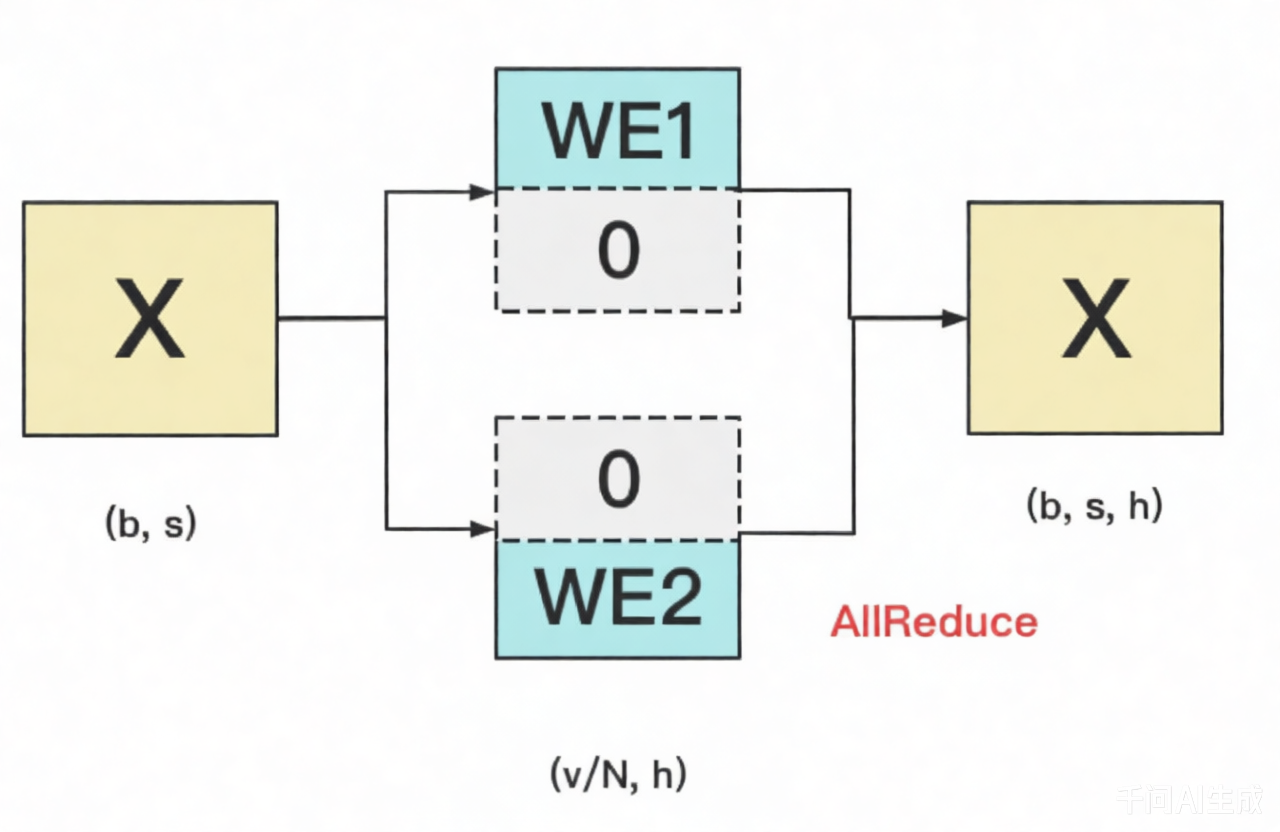
输入X过word embedding的前向过程,等价于用token的序号去word embedding中按行索引,是一个查表过程。
假设词表中有300个词,现在我们将word embedding拆分到两块GPU上,第一块GPU维护词表[0, 150),第二块GPU维护词表[150, 299)。当输入X去GPU上查找时,能找到的词,就正常返回词向量,找不到就把词向量中的全部全素都置0。按此方式查找完毕后,每块GPU上的数据做一次AllReduce,就能得到最终的输入。
对于输出层embedding来说,一般和embedding绑定共享参数,它把输入再映射回词表里,得到每一个位置的词。
此时前向计算就是将embedding矩阵分割到各个GPU上,并行计算矩阵乘法。具体计算过程如下:
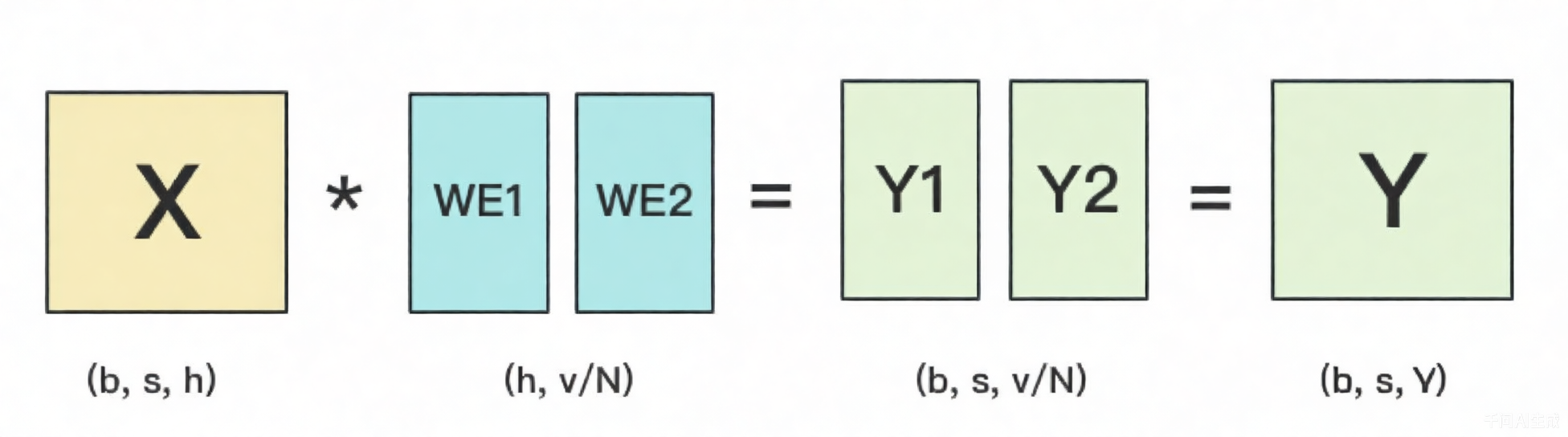
需要注意的是,当流水线并行大于1时,输入层和输出层不在同一个GPU上。因为输入层和输出层的embedding矩阵共享,所以反向传播时,需要通过AllReduce操作累加梯度。
Cross-entropy层
接着输出层计算损失函数。
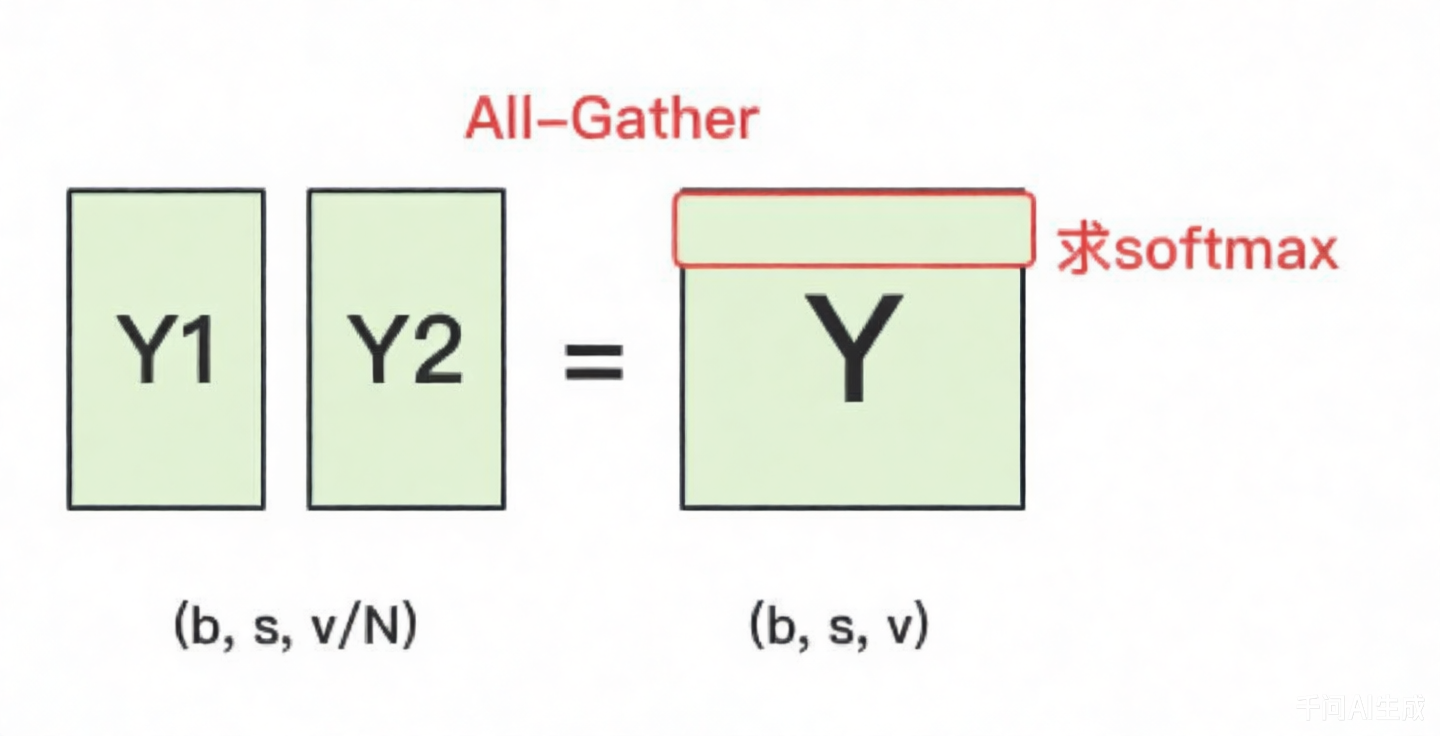
一种方式是对Y1和Y2做一次All-Gather,把它们concat起来形成Y,然后对Y的每一行做softmax,最后计算交叉熵损失。但这会产生额外的通信量,当词表很大时,开销也不容忽视。
另一种优化方式,如下:
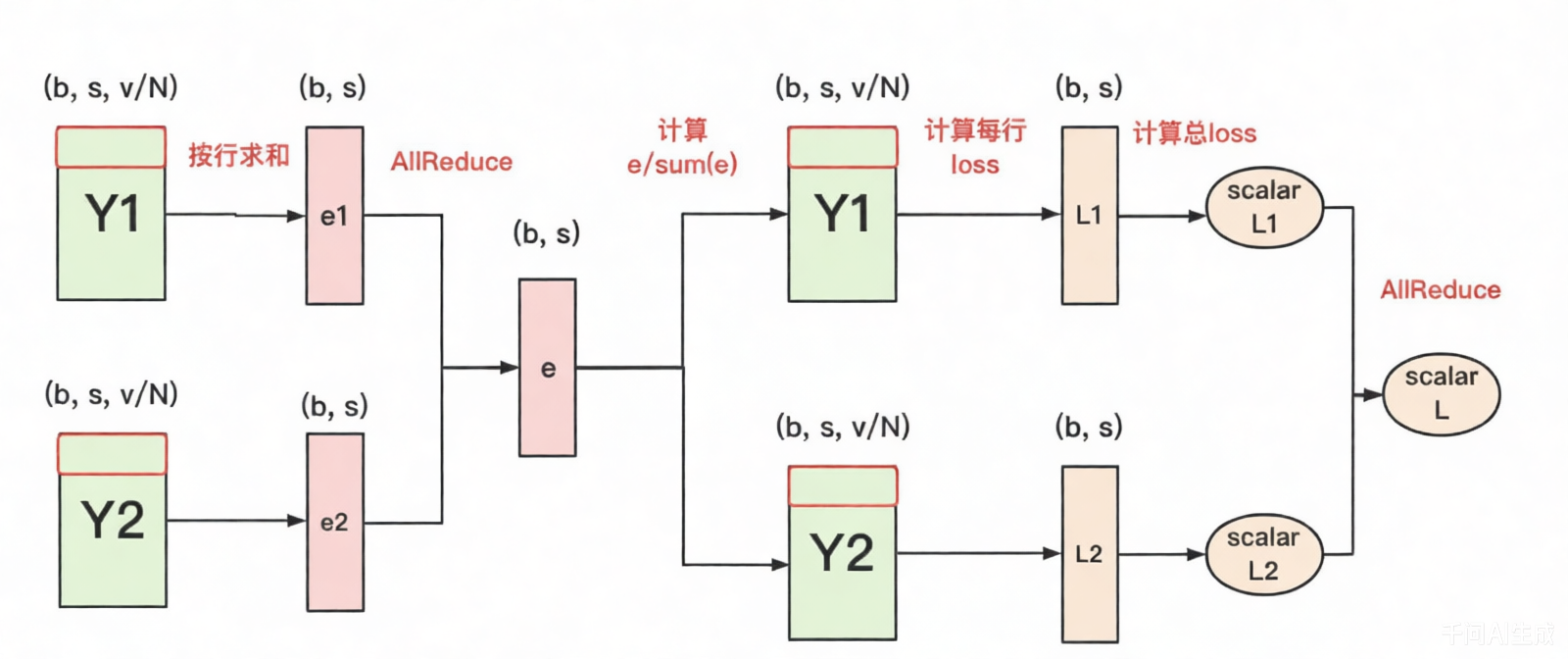
- 每块GPU上,先按行求和,得到各自GPU上的$GPU_sum(e)$
- 将每块GPU上结果做AllReduce,得到每行最终的$sum(e)$,也就softmax中的分母。此时的通讯量和词表大小无关,为$b*s$;
- 在每块GPU上,即可计算各自维护部分的$e_i/sum(e)$,将其与真值做cross-entropy,得到每行的loss,按行加总起来以后得到GPU上scalar Loss。
- 将各个GPU上的scalar Loss做AllReduce,得到总Loss。此时通讯量为GPU数量N。
Megatron实现
Magatron模型并行训练主要入口是pretrain 方法。该方法依次执行以下四件事:
- 初始化Megatron,重点是初始化分布式环境;
- 定义模型架构并切割模型,设置优化器和lr调度器;
- 构造train/val/test数据集;
- 训练模型;
Megatron 框架中的张量并行机制,其实现依赖于两个前提:其一是在分布式训练环境中构建用于张量切片通信的进程组;其二是在模型定义阶段就将权重和激活值按维度切分,使其天然适配多设备协同计算。
初始化分布式环境
不管是张量并行(TP),流水线并行(PP)还是数据并行(DP),都需要在不同GPU之间传递数据。GPU之间的通信关系是需要分组的,以执行不同的并行方式,这就是初始化分布式环境做的事。
假设我们有2台机器(node0和node1),每台机器上有8块GPU,GPU的编号为0~15。 我们使用这16块GPU,做DP/TP/PP混合并行,如下图
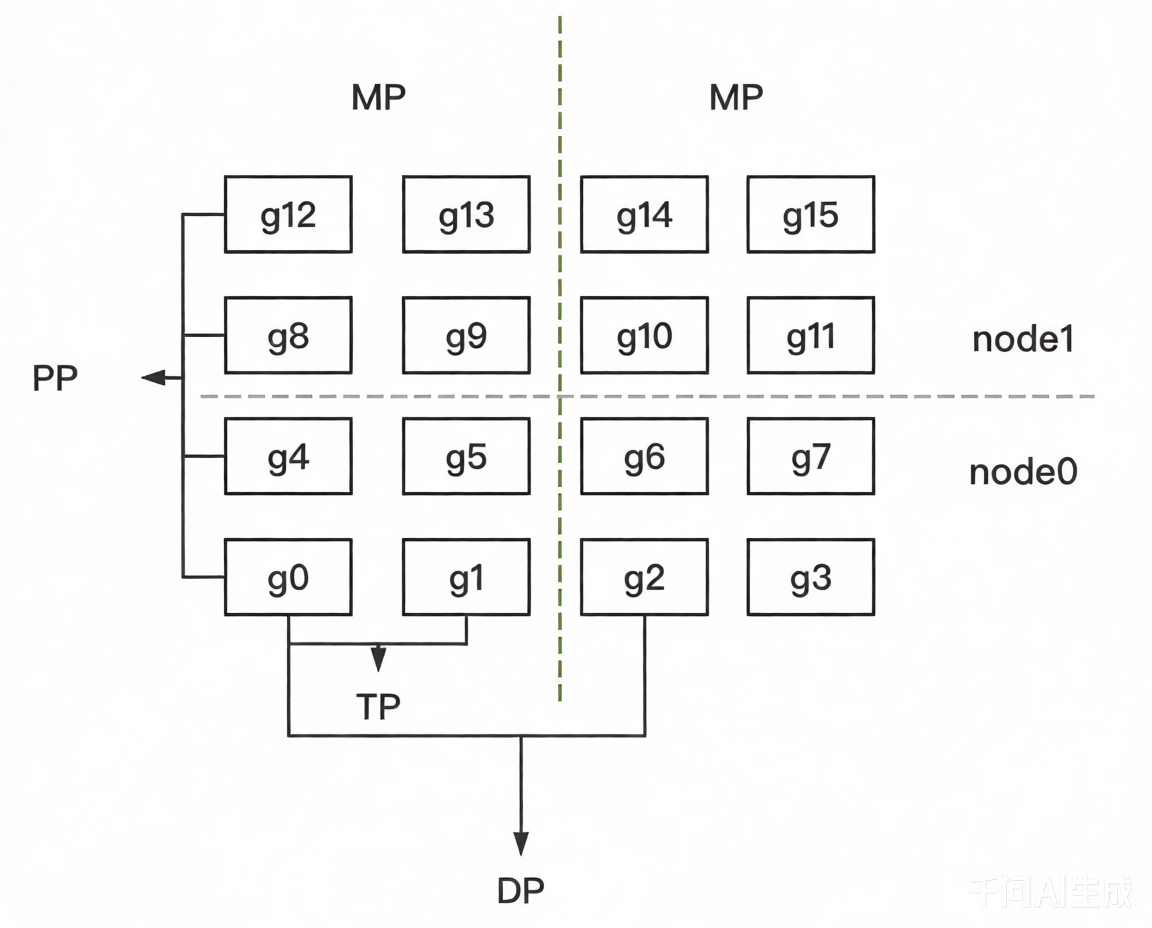
- MP:模型并行组(Model Parallism)。假设一个完整的模型需要布在8块GPU上,则如图所示,我们共布了2个model replica(2个MP)。MP组为:
[[g0, g1, g4, g5, g8, g9, g12, g13], [g2, g3, g6, g7, g10, g11, g14, g15]] - TP:张量并行组(Tensor Parallism)。对于一个模型的每一层,我们将其参数纵向切开,分别置于不同的GPU上,则图中一共有8个TP组。TP组为:
[[g0, g1], [g4, g5],[g8, g9], [g12, g13], [g2, g3], [g6, g7], [g10, g11], [g14, g15]] - PP:流水线并行组(Pipeline Parallism)。对于一个模型,我们将其每一层都放置于不同的GPU上,则图中一共有4个PP组。PP组为:
[[g0, g4, g8, g12], [g1, g5, g9, g13], [g2, g6, g10, g14], [g3, g7, g11, g15]] - DP:数据并行组(Data Parallism)。经过上述切割,对维护有相同模型部分的GPU,我们就可以做数据并行,则图中共有8个DP组。DP组为
[[g0, g2], [g1, g3], [g4, g6], [g5, g7], [g8, g10], [g9, g11], [g12, g14], [g13, g15]]
确认好DP/TP/PP组,并分配好进程后,每个进程独立执行自己所维护的那部分模型的计算,实现并行训练。
进一步地,对不同组能设置不同进程间的通讯方案。例如属于一个DP组的g0和g2需要进行梯度通讯,属于一个PP组的g4和g8需要进行层间输出结果的通讯。
回到pretrain函数,它的第一行就通过initialize_megatron执行了分布式初始化:
def pretrain(
train_valid_test_dataset_provider,
model_provider,
forward_step_func,
valid_forward_step_func=None,
extra_args_provider=None,
args_defaults={},
):
initialize_megatron(
extra_args_provider=extra_args_provider, args_defaults=args_defaults
)
...
总体来说,initialize_megatron这个方法实现了3个目的:
- 设置分布式环境:初始化进程,分配GPU,并设置进程大组(group)。也即例子中的0~15号进程同属一个分布式进程大组
- 制定DP/TP/PP分组策略,设置进程子组(subgroup)
- 设置DeepSpeed ZeRO-R,对activation进行优化
初始化进程大组
借助torch.distributed 来实现这一步,它是pytorch用于设置分布式训练环境的偏底层API(distributed communication package)。
init_method = "tcp://"
master_ip = os.getenv("MASTER_ADDR", "localhost") # 获取rank=0进程的ip
master_port = os.getenv("MASTER_PORT", "6000") # 获取rank=0进程的端口
init_method += master_ip + ":" + master_port
print(
f" > (rank={args.rank}) initializing process group: "
f"world_size={args.world_size} "
f"backend={args.distributed_backend} "
f"init_method={init_method}",
flush=True,
)
timeout = datetime.timedelta(minutes=args.dist_timeout)
torch.distributed.init_process_group(
backend=args.distributed_backend,
world_size=args.world_size,
rank=args.rank,
init_method=init_method,
timeout=timeout
)
print(f" > (rank={args.rank}) process group initialized")
设置DP/TP/PP组
设置完进程大组(group)后,我们就可以进一步设置进程子组(subgroup)了,也即设置DP/TP/PP组。
mpu.initialize_model_parallel( # megatron/mpu/initialize.py
args.tensor_model_parallel_size,
args.pipeline_model_parallel_size,
args.virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_size,
)
核心函数initialize_model_parallel 在megatron/mpu/initialize.py 下。mpu的含义是model parallisim utils,也就是和模型并行设置相关的函数,都放在这个目录下,它接收3个参数:
- tensor_model_parallel_size:每个TP组的进程数量。例如图例中是2
- pipeline_model_parallel_size:每个PP组的进程数量。例如图例中是4
- virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_size:每个virtual PP组的进程数量。这是NVIDIA对Megatron做后续迭代时提出的一种优化方法。我们之后会单独开一篇文章来讲解。这里可暂时忽略(不是必须参数,可以传None值)。
定好了TP和PP,DP_size就能根据 world_size // (TP_size * PP_size)计算得出。
def initialize_model_parallel(
tensor_model_parallel_size_=1,
pipeline_model_parallel_size_=1,
virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_size_=None,
):
"""
Initialize model data parallel groups.
Arguments:
tensor_model_parallel_size: number of GPUs used to parallelize model tensor.
pipeline_model_parallel_size: number of GPUs used to parallelize model pipeline.
Let's say we have a total of 16 GPUs denoted by g0 ... g15 and we
use 2 GPUs to parallelize the model tensor, and 4 GPUs to parallelize
the model pipeline. The present function will
create 8 tensor model-parallel groups, 4 pipeline model-parallel groups
and 8 data-parallel groups as:
8 data_parallel groups:
[g0, g2], [g1, g3], [g4, g6], [g5, g7], [g8, g10], [g9, g11], [g12, g14], [g13, g15]
8 tensor model-parallel groups:
[g0, g1], [g2, g3], [g4, g5], [g6, g7], [g8, g9], [g10, g11], [g12, g13], [g14, g15]
4 pipeline model-parallel groups:
[g0, g4, g8, g12], [g1, g5, g9, g13], [g2, g6, g10, g14], [g3, g7, g11, g15]
2 model-parallel group:
[g0, g1, g4, g5, g8, g9, g12, g13], [g2, g3, g6, g7, g10, g8, g14, g15]
Note that for efficiency, the caller should make sure adjacent ranks
are on the same DGX box. For example if we are using 2 DGX-1 boxes
with a total of 16 GPUs, rank 0 to 7 belong to the first box and
ranks 8 to 15 belong to the second box.
"""
if torch.distributed.get_rank() == 0:
print(
"> initializing tensor model parallel with size {}".format(
tensor_model_parallel_size_
)
)
print( # 打印出流水线模型并行的度
"> initializing pipeline model parallel with size {}".format(
pipeline_model_parallel_size_
)
)
# Get world size and rank. Ensure some consistencies.
assert torch.distributed.is_initialized() # 确保torch已经做了分布式初始化
world_size = torch.distributed.get_world_size() # 得到全局进程的总数
tensor_model_parallel_size = min(tensor_model_parallel_size_, world_size)
pipeline_model_parallel_size = min(pipeline_model_parallel_size_, world_size)
ensure_divisibility( # 后者表示一个完整模型所占的gpu数,我们要保证前者能被后者整除
world_size, tensor_model_parallel_size * pipeline_model_parallel_size
)
# 在codegeex中,TP_size=8, PP_size=1,world_size = 1536,因此DP_size是1536/(8*1) = 192
data_parallel_size = world_size // ( # 根据TP_size和PP_size,求出DP_size
tensor_model_parallel_size * pipeline_model_parallel_size
)
num_tensor_model_parallel_groups = world_size // tensor_model_parallel_size # TP的组数
num_pipeline_model_parallel_groups = world_size // pipeline_model_parallel_size # PP的组数
num_data_parallel_groups = world_size // data_parallel_size # DP的组数
if virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_size_ is not None:
global _VIRTUAL_PIPELINE_MODEL_PARALLEL_RANK
global _VIRTUAL_PIPELINE_MODEL_PARALLEL_WORLD_SIZE
_VIRTUAL_PIPELINE_MODEL_PARALLEL_RANK = 0
_VIRTUAL_PIPELINE_MODEL_PARALLEL_WORLD_SIZE = (
virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_size_
)
rank = torch.distributed.get_rank() # 获取当前进程的全局rank
# Build the data-parallel groups.(设置DP组)
global _DATA_PARALLEL_GROUP # 保存DP组,如[[0,2], [1,3]...],数字表示进进程的全局序号
assert _DATA_PARALLEL_GROUP is None, "data parallel group is already initialized"
all_data_parallel_group_ranks = []
for i in range(pipeline_model_parallel_size):
start_rank = i * num_pipeline_model_parallel_groups
end_rank = (i + 1) * num_pipeline_model_parallel_groups
for j in range(tensor_model_parallel_size):
ranks = range(start_rank + j, end_rank, tensor_model_parallel_size)
all_data_parallel_group_ranks.append(list(ranks))
group = torch.distributed.new_group(ranks) # 设置DP组
if rank in ranks:
_DATA_PARALLEL_GROUP = group
# Build the model-parallel groups.(设置MP组)
global _MODEL_PARALLEL_GROUP # 保存MP组
assert _MODEL_PARALLEL_GROUP is None, "model parallel group is already initialized"
for i in range(data_parallel_size):
ranks = [
data_parallel_group_ranks[i]
for data_parallel_group_ranks in all_data_parallel_group_ranks
]
group = torch.distributed.new_group(ranks) # 设置MP组
if rank in ranks:
_MODEL_PARALLEL_GROUP = group
# Build the tensor model-parallel groups.(设置TP组)
global _TENSOR_MODEL_PARALLEL_GROUP # 保存TP组
assert (
_TENSOR_MODEL_PARALLEL_GROUP is None
), "tensor model parallel group is already initialized"
for i in range(num_tensor_model_parallel_groups):
ranks = range(
i * tensor_model_parallel_size, (i + 1) * tensor_model_parallel_size
)
group = torch.distributed.new_group(ranks) # 设置TP组
if rank in ranks:
_TENSOR_MODEL_PARALLEL_GROUP = group
# Build the pipeline model-parallel groups and embedding groups
# (first and last rank in each pipeline model-parallel group).(设置PP组与embedding组)
global _PIPELINE_MODEL_PARALLEL_GROUP # 设置PP组
global _PIPELINE_GLOBAL_RANKS
assert (
_PIPELINE_MODEL_PARALLEL_GROUP is None
), "pipeline model parallel group is already initialized"
global _EMBEDDING_GROUP
assert _EMBEDDING_GROUP is None, "embedding group is already initialized"
for i in range(num_pipeline_model_parallel_groups):
ranks = range(i, world_size, num_pipeline_model_parallel_groups)
group = torch.distributed.new_group(ranks) # 设置PP组
if rank in ranks:
_PIPELINE_MODEL_PARALLEL_GROUP = group
_PIPELINE_GLOBAL_RANKS = ranks
# Setup embedding group (to exchange gradients between
# first and last stages).
if len(ranks) > 1:
embedding_ranks = [ranks[0], ranks[-1]]
else:
embedding_ranks = ranks
group = torch.distributed.new_group(embedding_ranks) # 设置embedding组
if rank in embedding_ranks:
_EMBEDDING_GROUP = group
总结来说,我们采用torch.distributed.new_group(ranks) 在进程大组下设置子组。ranks是list of list,表示对进程序号的划分,例如设置DP组,则ranks为[[0,2], [1,3]...],以此类推。我们将划分结果存在全局变量中(例如_DATA_PARALLEL_GROUP),方便我们在后续切割模型时使用。
同时,我们定义以下函数,使得对于任意一个进程,我们都能查到它在DP/TP/PP组中的局部序号(local_rank),以及它对应的DP/TP/PP组的world_size。
Q:如何确保逻辑分组和物理GPU对应上,使得TP、DP尽量跑在同一个节点上?
A:torchrun能够确保rank按照节点连续分配,只要TP size不超过节点GPU数量,TP天然跑在同一个节点。
模型定义和切分
setup_model_and_optimizer是整个模型并行的入口函数,如下图,它主要由”定义模型架构并切割模型“,“设置optimizer”和“设置学习率”三部分组成。我们关注的重点在第一部分上(get_model)。
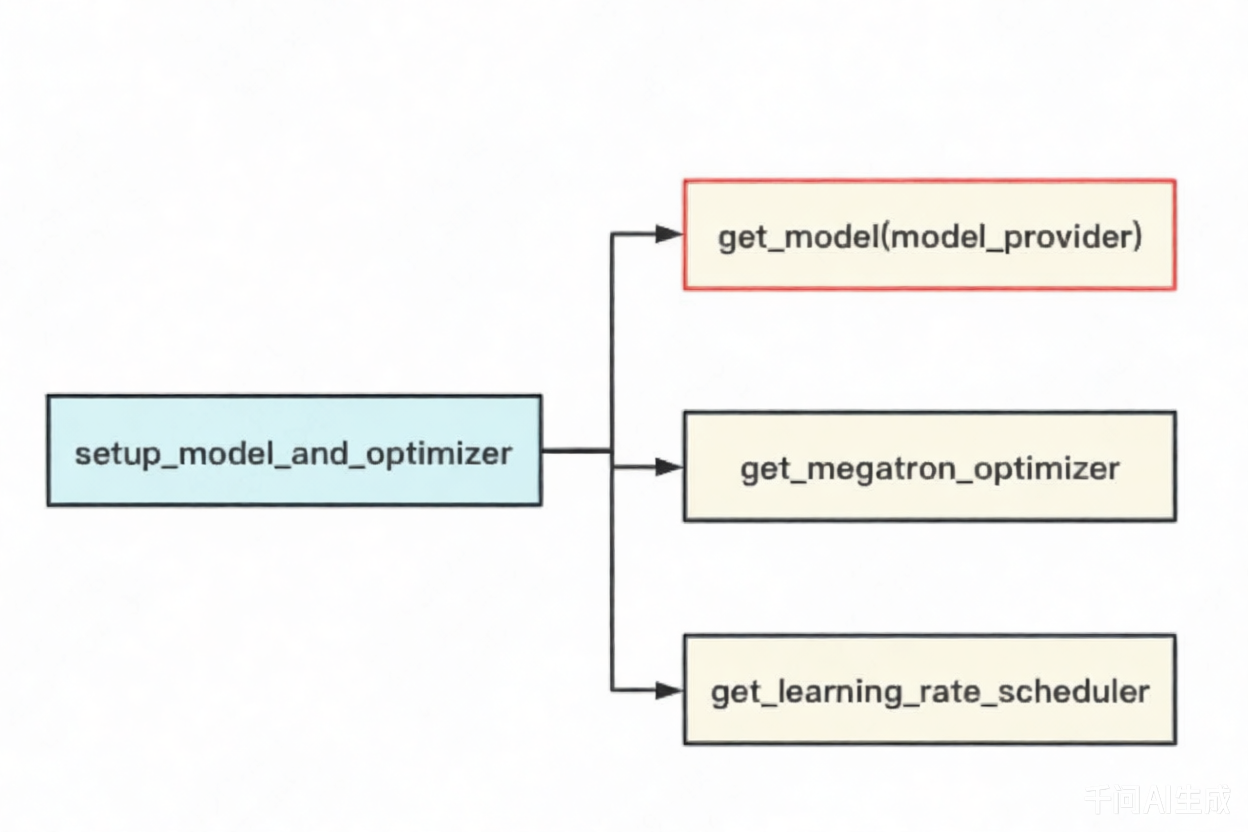
get_model(model_provider) 函数主要做了两件事:
- 在CPU上定义模型。
model_provider是一个函数,调用它即可返回Megatron的分布式模型,也就是一个MegatronModule类的子类,这个将是下文要介绍的重点。 - 把模型从CPU搬运至GPU上。这里有两种方法可供选择:
- 方案一:借助deepspeed进行管理。
- 方案二:手动搬运管理。这里需要我们以下事情:
- 显式搬运。即手动将模型搬运到当前进程所对应的GPU上。
- 权重精度设定。
- 初始化DP组。这里指的是定义DP组间forward、backward和梯度计算与通讯等方法。在Megatron中,TP和PP组的这些方法是人为定义的,而DP组则是可以用现成的(torch的DistributedDataParallel)。
在 Megatron 中,模型并行所需的张量分割与通信操作内嵌于模型定义之中,这里实现的模型就是Megatron的分布式模型。MegatronModule 是所有分布式模型和组件的基类,统一了模型组件的接口,并为模型并行(Model Parallelism)及训练/推理流程提供核心支持。
模型切分的基本原理,是利用可获取到的进程ID(全局或DP/TP/PP组内的),在不同进程依靠类似if..else.. 来解决模型差异化问题。
有两种方式对模型进行切割:
- 方案一:先定义出完整的模型,并对模型参数做初始化,然后根据进程id取出相应子模型,搬运到GPU上
- 方案二:直接根据进程id,设计好当前子模型,做参数初始化,搬运到GPU上
这两者从结果上可以等价,它们的核心差别,在于“随机种子”的设定,它关系到模型是否能够复现。例如,对于Word Embedding来说,切分的WE1和WE2间需要采用不同的随机种子。因为若采用相同的随机种子,则WE1和WE2的结果完全一样,这不等价于先随机初始化WE,再将它进行切割。
一般在TP/PP组内,设定不同的随机种子。而在DP组内,设定相同的随机种子。
方案1(先做整体初始化再切割)在代码里被称为“CPU上的初始化”(_initialize_affine_weight_cpu)。
def _initialize_affine_weight_cpu(
weight,
output_size,
input_size,
per_partition_size,
partition_dim,
init_method,
stride=1,
return_master_weight=False,
):
"""Initialize affine weight for model parallel.
Build the master weight on all processes and scatter
the relevant chunk."""
set_tensor_model_parallel_attributes(
tensor=weight, is_parallel=True, dim=partition_dim, stride=stride
)
# Initialize master weight
# 先初始化完整的master_weight,比传入的weight大
master_weight = torch.empty(
output_size, input_size, dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=False
)
init_method(master_weight)
args = get_args()
master_weight = master_weight.to(dtype=args.params_dtype)
# Split and copy
per_partition_per_stride_size = divide(per_partition_size, stride)
weight_list = torch.split(
master_weight, per_partition_per_stride_size, dim=partition_dim
)
rank = get_tensor_model_parallel_rank()
world_size = get_tensor_model_parallel_world_size()
my_weight_list = weight_list[rank::world_size]
with torch.no_grad():
torch.cat(my_weight_list, dim=partition_dim, out=weight) # 传入的weight是在cpu上创建的
if return_master_weight:
return master_weight
return None
方案2(直接对局部初始化)被称为“在GPU上的初始化”(_initialize_affine_weight_gpu)。
def _initialize_affine_weight_gpu(weight, init_method, partition_dim, stride=1):
"""Initialize affine weight for model parallel on GPU."""
set_tensor_model_parallel_attributes(
tensor=weight, is_parallel=True, dim=partition_dim, stride=stride
)
if ds_checkpointing.is_configured():
global get_cuda_rng_tracker
get_cuda_rng_tracker = ds_checkpointing.get_cuda_rng_tracker
with get_cuda_rng_tracker().fork():
init_method(weight) # 传入的weight在GPU上创建了,直接初始化
通过use_cpu_initialization参数控制权重初始化方法,当使用“在GPU上的初始化”时,权重其实已经被搬运到GPU上了。
就像pytorch里的复杂模型是由一些基础模块组合而来一样,Megatron里的分布式模型也由一些基础模块组成,这些组件就好比pytorch里组件的“并行版”,完成了张量并行和流水线并行的实现。
以下介绍Megatron中常见的分布式模型组件的定义,而更为复杂的分布式Transformer层和具体的LLM模型,不过是这些基础的组件搭成的。
Embedding
Emebdding类定义了word/position/segment embedding,并定义输入X过embedding层的计算方法。
class Embedding(MegatronModule):
"""Language model embeddings.
Arguments:
hidden_size: hidden size
vocab_size: vocabulary size
max_sequence_length: maximum size of sequence. This
is used for positional embedding
embedding_dropout_prob: dropout probability for embeddings
init_method: weight initialization method
num_tokentypes: size of the token-type embeddings. 0 value
will ignore this embedding
"""
def __init__(
self,
hidden_size, # 每个token的向量维度
vocab_size, # 词表大小
max_sequence_length, # 最长序列长度
embedding_dropout_prob, # dropout probability for embeddings
init_method, # 初始化权重的方法
num_tokentypes=0, # 类似于Bert中的segment type
):
super(Embedding, self).__init__()
args = get_args()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.init_method = init_method
self.num_tokentypes = num_tokentypes
self.max_sequence_length = max_sequence_length
# WE size: (vocab_size//TP_N, hidden_size)
# TP_N表示TP组模型并行度
self.word_embeddings = mpu.VocabParallelEmbedding(
vocab_size, self.hidden_size, init_method=self.init_method)
self._word_embeddings_key = 'word_embeddings'
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
# PE size: (max_seq_len, hidden_size)
self.position_embeddings = torch.nn.Embedding(
max_sequence_length, self.hidden_size)
self.position_embeddings = self.position_embeddings.half()
self._position_embeddings_key = 'position_embeddings'
# Initialize the position embeddings.
self.init_method(self.position_embeddings.weight)
# TE_size:(num_tokentypes, hidden_size)
# TE类似于Bert中的segment embedding
self._tokentype_embeddings_key = 'tokentype_embeddings'
if self.num_tokentypes > 0:
self.tokentype_embeddings = torch.nn.Embedding(self.num_tokentypes,
self.hidden_size)
# Initialize the token-type embeddings.
self.init_method(self.tokentype_embeddings.weight)
else:
self.tokentype_embeddings = None
# Embeddings dropout
self.embedding_dropout = torch.nn.Dropout(embedding_dropout_prob)
def add_tokentype_embeddings(self, num_tokentypes):
"""如果在pretrain阶段未定义TE,而在fine-tune阶段TE,则可通过此函数添加
"""
if self.tokentype_embeddings is not None:
raise Exception('tokentype embeddings is already initialized')
if torch.distributed.get_rank() == 0:
print('adding embedding for {} tokentypes'.format(num_tokentypes),
flush=True)
self.num_tokentypes = num_tokentypes
self.tokentype_embeddings = torch.nn.Embedding(num_tokentypes,
self.hidden_size)
# Initialize the token-type embeddings.
self.init_method(self.tokentype_embeddings.weight)
def forward(self, input_ids, position_ids, tokentype_ids=None):
"""定义输入X过embedding层的计算方法
"""
# words_embeddings size = (b, seq_len, hidden_size)
# 再次注意:self.word_embeddings做forward时,最终的输出结果是AllReduce的
words_embeddings = self.word_embeddings(input_ids)
# position_embeddings size = (b, seq_len, hidden_size)
position_embeddings = self.position_embeddings(position_ids)
# embedding = WE + PE
# embedding size = (b, seq_len, hidden_size)
embeddings = words_embeddings + position_embeddings
# 依需要决定是否增加TE
if tokentype_ids is not None:
assert self.tokentype_embeddings is not None
embeddings = embeddings + self.tokentype_embeddings(tokentype_ids)
else:
assert self.tokentype_embeddings is None
# Dropout.
embeddings = self.embedding_dropout(embeddings)
return embeddings
def state_dict_for_save_checkpoint(
self, destination=None, prefix='', keep_vars=False,
):
"""For easy load.
在模型训练过程中及时读取当前参数,方便及时保存(做checkpoint)
篇幅限制,这里不展示细节
"""
...
def load_state_dict(self, state_dict, strict=True):
"""Customized load.
用于模型的重载。例如训到一半挂掉了,我们就重新初始化一个新模型,
重载上个checkpoint保存下的权重。
篇幅限制,这里不展示细节
"""
...
可以看到,分布式Embedding的的实现依靠VocabParallelEmbedding 对象,其定义如下:
class VocabParallelEmbedding(torch.nn.Module):
"""Embedding parallelized in the vocabulary dimension.
This is mainly adapted from torch.nn.Embedding and all the default
values are kept.
Arguments:
num_embeddings: vocabulary size.
embedding_dim: size of hidden state.
init_method: method to initialize weights.
"""
def __init__(self, num_embeddings, embedding_dim, init_method=init.xavier_normal_):
super(VocabParallelEmbedding, self).__init__()
# Keep the input dimensions.
self.num_embeddings = num_embeddings # vocab_size
self.embedding_dim = embedding_dim # hidden_state.
# Set the detauls for compatibility.
self.padding_idx = None
self.max_norm = None
self.norm_type = 2.0
self.scale_grad_by_freq = False
self.sparse = False
self._weight = None
# 当前进程所在TP组进程总数
self.tensor_model_parallel_size = get_tensor_model_parallel_world_size()
# 根据当前进程在TP组中的序号,确定其所需维护的WE部分,沿着vocab维度对WE进行切割
# 例如,进程id=0, 维护词表序号[0,5)范围内的数据;进程id=1,维护[5,10)
(
self.vocab_start_index,
self.vocab_end_index,
) = VocabUtility.vocab_range_from_global_vocab_size(
self.num_embeddings,
get_tensor_model_parallel_rank(),
self.tensor_model_parallel_size,
)
# 计算当前进程维护的词表大小
self.num_embeddings_per_partition = (
self.vocab_end_index - self.vocab_start_index
)
# 对WE做初始化
args = get_args() # 读取预训练参数配置
if args.use_cpu_initialization: # CPU上做初始化
self.weight = Parameter( # 在CPU上先生成一个完整的WE
torch.empty(
self.num_embeddings_per_partition,
self.embedding_dim,
dtype=args.params_dtype,
# dtype=torch.float32,
)
)
# 对CPU上的WE做切割(随机种子在初始化分布式中已设定好,不用变)
_initialize_affine_weight_cpu(
self.weight,
self.num_embeddings,
self.embedding_dim,
self.num_embeddings_per_partition,
0,
init_method, # 初始化权重的方法,例如xavier之类
)
else: # 在GPU上做初始化
self.weight = Parameter( # 生成一个切割好的WE
torch.empty(
self.num_embeddings_per_partition,
self.embedding_dim,
device=torch.cuda.current_device(),
dtype=args.params_dtype,
# dtype=torch.float32,
)
)
# 在GPU上做初始化,注意TP组内不同进程采用不同的随机种子
_initialize_affine_weight_gpu(
self.weight, init_method, partition_dim=0, stride=1
)
def forward(self, input_):
"""定义输入X过WE的计算方法,输出结果已经过AllReduce"""
if self.tensor_model_parallel_size > 1: # 如果使用TP
# 如果在当前进程维护的WE上,找不到对应的单词,那么对应位置就赋0
# 例如当前的数据的tokenid是:[2,7,1,5],当前维护的词表是[0,1,2](start_index=0, end_index = 3),
# 则mask之后的数据为[2,0,1,0]
# Build the mask.
input_mask = (input_ < self.vocab_start_index) | (
input_ >= self.vocab_end_index
)
# Mask the input.
masked_input = input_.clone() - self.vocab_start_index
masked_input[input_mask] = 0
else:
masked_input = input_
# 输入X,过当前进程维护的部分WE的结果
output_parallel = F.embedding(
masked_input, # tensor containing indices into the embedding matrix
self.weight, # 切割好的word embedding的权重
self.padding_idx,
self.max_norm,
self.norm_type,
self.scale_grad_by_freq,
self.sparse,
)
# 当前词表不维护的部分,都设为0
if self.tensor_model_parallel_size > 1:
output_parallel[input_mask, :] = 0.0 #
# 将TP组各GPU上的结果做AllReduce
output = reduce_from_tensor_model_parallel_region(output_parallel)
return output
def _initialize_affine_weight_cpu(...):
"""CPU版权重初始化。这个不难,大家可以自己阅读"""
...
def _initialize_affine_weight_gpu(...):
"""GPU版权重初始化。特别关注设置随机种子部分"""
...
# 借助deepspeed或自定义的get_cuda_rng_tracker方法,对随机种子进行操作
# get_cuda_rng_tracker细节,大家可自行阅读源码
if ds_checkpointing.is_configured():
global get_cuda_rng_tracker
get_cuda_rng_tracker = ds_checkpointing.get_cuda_rng_tracker
with get_cuda_rng_tracker().fork():
init_method(weight)
ParallelSelfAttention
由前文的原理可知,对QKV矩阵,采用“列切分”,对线性矩阵B,采用“行切分”。这样设计的好处是,在经过QKV的计算后,各进程在不用通讯的前提下,继续做线性计算,直到最后一步才AllReduce,起到降低通讯成本的作用。
列切分矩阵乘法的定义,如下:
class ColumnParallelLinear(torch.nn.Module):
"""Linear layer with column parallelism.
The linear layer is defined as Y = XA + b. A is parallelized along
its second dimension as A = [A_1, ..., A_p].
Arguments:
input_size: first dimension of matrix A.
output_size: second dimension of matrix A.
bias: If true, add bias
gather_output: If true, call all-gether on output and make Y avaiable
to all GPUs, otherwise, every GPU will have its output
which is Y_i = XA_i
init_method: method to initialize weights. Note that bias is always set
to zero.
stride: For the strided linear layers.
keep_master_weight_for_test: This was added for testing and should be
set to False. It returns the master weights
used for initialization.
skip_bias_add: This was added to enable performance optimations where bias
can be fused with other elementwise operations. we skip
adding bias but instead return it.
"""
# 该类定义了切割后的权重W,例如切割后的W1和W2都可分别视为该类的一个实例
def __init__(
self,
input_size, # W的第一个维度
output_size, # W的第二个维度
bias=True, # 是否需要引入bias
gather_output=True, # 决定是否要将Y1和Y2做all-gather
init_method=init.xavier_normal_,
stride=1,
keep_master_weight_for_test=False,
skip_bias_add=False,
params_dtype=None,
skip_init=False,
device=None,
):
super(ColumnParallelLinear, self).__init__()
# Keep input parameters
self.input_size = input_size
self.output_size = output_size
self.gather_output = gather_output
# Divide the weight matrix along the last dimension.
# 当前进程所在TP组的总进程数
world_size = get_tensor_model_parallel_world_size()
# 每块GPU上维护的hidden_size的大小,等于 原hidden_zize // TP组总进程数
self.output_size_per_partition = divide(output_size, world_size)
self.skip_bias_add = skip_bias_add
self.params_dtype = params_dtype
self.device = device
# Parameters.
# Note: torch.nn.functional.linear performs XA^T + b and as a result
# Initialize weight.
args = get_args() # 取得命令行所有的参数
if not skip_init:
if args.use_cpu_initialization: # CPU上初始化
self.weight = Parameter(
torch.empty(
self.output_size_per_partition,
self.input_size,
dtype=self.params_dtype if self.params_dtype is not None else args.params_dtype,
)
)
self.master_weight = _initialize_affine_weight_cpu( #
self.weight,
self.output_size,
self.input_size,
self.output_size_per_partition,
0,
init_method,
stride=stride,
return_master_weight=keep_master_weight_for_test,
)
else: # GPU上初始化
self.weight = Parameter(
torch.empty(
self.output_size_per_partition,
self.input_size,
device=self.device if self.device is not None else torch.cuda.current_device(),
dtype=self.params_dtype if self.params_dtype is not None else args.params_dtype,
)
)
_initialize_affine_weight_gpu(
self.weight, init_method, partition_dim=0, stride=stride
)
else:
self.register_parameter("weight", None)
# 对bias做处理,道理同weight
if bias and not skip_init:
if args.use_cpu_initialization: # CPU上初始化
self.bias = Parameter(
torch.empty(self.output_size_per_partition,
dtype=self.params_dtype if self.params_dtype is not None else args.params_dtype)
)
else:
self.bias = Parameter( # GPU上初始化
torch.empty(
self.output_size_per_partition,
device=self.device if self.device is not None else torch.cuda.current_device(),
dtype=self.params_dtype if self.params_dtype is not None else args.params_dtype,
)
)
set_tensor_model_parallel_attributes(self.bias, True, 0, stride)
# Always initialize bias to zero.
with torch.no_grad():
self.bias.zero_()
else:
self.register_parameter("bias", None)
def forward(self, input_):
# 定义列切割中的f算子
# 调用copy_to_tensor_model_parallel_region则新建一个_CopyToModelParallelRegion实例(见下)
input_parallel = copy_to_tensor_model_parallel_region(input_)
bias = self.bias if not self.skip_bias_add else None # 定义bias
output_parallel = F.linear(input_parallel, self.weight, bias) # X * 切割好的权重
# 决定是否要对每个进程上的输出结果做All-Reduce
if self.gather_output:
# 定义列切割中的g算子
# 调用gather_from_tensor_model_parallel_region则新建一个_GatherFromModelParallelRegion实例(见下)
output = gather_from_tensor_model_parallel_region(output_parallel) # 把各GPU上的输出按照列gather起来后,作为最终输出
else:
output = output_parallel # 否则最终输出还是自己算的那块GPU
output_bias = self.bias if self.skip_bias_add else None
return output, output_bias
# 列切割中的f与g
class _CopyToModelParallelRegion(torch.autograd.Function):
"""Pass the input to the model parallel region."""
# 列切割下的f算子
# forward:copy输入
# backward:对梯度做AllReduce
@staticmethod
def symbolic(graph, input_):
return input_
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, input_):
return input_
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
return _reduce(grad_output)
class _GatherFromModelParallelRegion(torch.autograd.Function):
"""Gather the input from model parallel region and concatinate."""
# 列切割中的g算子
# forward:All-Gather输出
# backward:对梯度,沿着列方向做split
@staticmethod
def symbolic(graph, input_):
return _gather(input_)
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, input_):
return _gather(input_)
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
return _split(grad_output)
行切分矩阵乘法的定义,如下:
class RowParallelLinear(torch.nn.Module):
"""Linear layer with row parallelism.
The linear layer is defined as Y = XA + b. A is parallelized along
its first dimension and X along its second dimension as:
- -
| A_1 |
| . |
A = | . | X = [X_1, ..., X_p]
| . |
| A_p |
- -
Arguments:
input_size: first dimension of matrix A.
output_size: second dimension of matrix A.
bias: If true, add bias. Note that bias is not parallelized.
input_is_parallel: If true, we assume that the input is already
split across the GPUs and we do not split
again.
init_method: method to initialize weights. Note that bias is always set
to zero.
stride: For the strided linear layers.
keep_master_weight_for_test: This was added for testing and should be
set to False. It returns the master weights
used for initialization.
skip_bias_add: This was added to enable performance optimations where bias
can be fused with other elementwise operations. we skip
adding bias but instead return it.
"""
def __init__(
self,
input_size,
output_size,
bias=True,
input_is_parallel=False,
init_method=init.xavier_normal_,
stride=1,
keep_master_weight_for_test=False,
skip_bias_add=False,
params_dtype=None,
skip_init=False,
device=None,
):
super(RowParallelLinear, self).__init__()
# Keep input parameters
self.input_size = input_size
self.output_size = output_size
self.input_is_parallel = input_is_parallel
# Divide the weight matrix along the last dimension.
world_size = get_tensor_model_parallel_world_size()
self.input_size_per_partition = divide(input_size, world_size)
self.skip_bias_add = skip_bias_add
self.params_dtype = params_dtype
self.device = device
# Parameters.
# Note: torch.nn.functional.linear performs XA^T + b and as a result
# we allocate the transpose.
# Initialize weight.
args = get_args()
if not skip_init:
if args.use_cpu_initialization:
self.weight = Parameter(
torch.empty(
self.output_size,
self.input_size_per_partition,
dtype=self.params_dtype if self.params_dtype is not None else args.params_dtype,
)
)
self.master_weight = _initialize_affine_weight_cpu(
self.weight,
self.output_size,
self.input_size,
self.input_size_per_partition,
1,
init_method,
stride=stride,
return_master_weight=keep_master_weight_for_test,
)
else:
self.weight = Parameter(
torch.empty(
self.output_size,
self.input_size_per_partition,
device=self.device if self.device is not None else torch.cuda.current_device(),
dtype=self.params_dtype if self.params_dtype is not None else args.params_dtype,
)
)
_initialize_affine_weight_gpu(
self.weight, init_method, partition_dim=1, stride=stride
)
else:
self.register_parameter("weight", None)
if bias and not skip_init:
if args.use_cpu_initialization:
self.bias = Parameter(
torch.empty(self.output_size,
dtype=self.params_dtype if self.params_dtype is not None else args.params_dtype)
)
else:
self.bias = Parameter(
torch.empty(
self.output_size,
device=self.device if self.device is not None else torch.cuda.current_device(),
dtype=self.params_dtype if self.params_dtype is not None else args.params_dtype,
)
)
# Always initialize bias to zero.
with torch.no_grad():
self.bias.zero_()
else:
self.register_parameter("bias", None)
def forward(self, input_):
# Set up backprop all-reduce.
if self.input_is_parallel:
input_parallel = input_
else:
input_parallel = scatter_to_tensor_model_parallel_region(input_)
# Matrix multiply.
output_parallel = F.linear(input_parallel, self.weight)
# All-reduce across all the partitions.
output_ = reduce_from_tensor_model_parallel_region(output_parallel)
if not self.skip_bias_add:
output = output_ + self.bias if self.bias is not None else output_
output_bias = None
else:
output = output_
output_bias = self.bias
return output, output_bias
# 行切割中的f和g算子
class _ScatterToModelParallelRegion(torch.autograd.Function):
"""Split the input and keep only the corresponding chuck to the rank."""
# 行切割中的f算子
# forward:沿列split输入
# backward:all-gather梯度
@staticmethod
def symbolic(graph, input_):
return _split(input_)
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, input_):
return _split(input_)
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
return _gather(grad_output)
class _ReduceFromModelParallelRegion(torch.autograd.Function):
"""All-reduce the input from the model parallel region."""
# 行切割中的g算子
# forward:AllReduce输出
# backward:正常计算梯度,GPU间无需做任何通讯
@staticmethod
def symbolic(graph, input_):
return _reduce(input_)
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, input_):
return _reduce(input_)
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
return grad_output
ParallelSelfAttention 类由“列切分”ColumnParallelLinear和“行切分”RowParallelLinear组合而来。
class ParallelSelfAttention(MegatronModule):
"""Parallel self-attention layer abstract class.
Self-attention layer takes input with size [b, s, h]
and returns output of the same size.
"""
def __init__(self, init_method,
output_layer_init_method, layer_number):
super(ParallelSelfAttention, self).__init__()
args = get_args()
self.fp16 = args.fp16
self.attention_softmax_in_fp32 = args.attention_softmax_in_fp32
self.layer_number = max(1, layer_number)
# Per attention head and per partition values.
world_size = mpu.get_model_parallel_world_size()
self.hidden_size_per_partition = mpu.divide(
args.hidden_size // 2 if args.compress else args.hidden_size,
world_size)
self.hidden_size_per_attention_head = mpu.divide(
args.hidden_size // 2 if args.compress else args.hidden_size, args.num_attention_heads)
self.num_attention_heads_per_partition = mpu.divide(
args.num_attention_heads, world_size)
if hasattr(args, 'attention_upweight'):
self.attention_upweight = args.attention_upweight
else:
self.attention_upweight = None
# Strided linear layer.
self.query = mpu.ColumnParallelLinear(
args.hidden_size,
args.hidden_size // 2 if args.compress else args.hidden_size,
gather_output=False,
init_method=init_method)
self.key = mpu.ColumnParallelLinear(
args.hidden_size,
args.hidden_size // 2 if args.compress else args.hidden_size,
gather_output=False,
init_method=init_method)
self.value = mpu.ColumnParallelLinear(
args.hidden_size,
args.hidden_size // 2 if args.compress else args.hidden_size,
gather_output=False,
init_method=init_method)
self.norm_factor = math.sqrt(self.hidden_size_per_attention_head)
self.softmax = torch.nn.Softmax(dim=-1)
# Dropout. Note that for a single iteration, this layer will generate
# different outputs on different number of parallel partitions but
# on average it should not be partition dependent.
self.attention_dropout = torch.nn.Dropout(args.attention_dropout)
# Output.
self.dense = mpu.RowParallelLinear(
args.hidden_size // 2 if args.compress else args.hidden_size,
args.hidden_size,
input_is_parallel=True if args.tensor_model_parallel_size > 1 else False,
init_method=output_layer_init_method,
skip_bias_add=True)
def forward(
self,
hidden_states,
attention_mask,
layer_past=None,
get_key_value=False,
prompt_length=None,
context_length=None,
):
# hidden_states: [sq, b, h]
# =====================
# Query, Key, and Value
# =====================
...
ParallelMLP
分布式MLP也是由ColumnParallelLinear和RowParallelLinear基础组件构成。
class ParallelMLP(MegatronModule):
"""MLP.
MLP will take the input with h hidden state, project it to 4*h
hidden dimension, perform nonlinear transformation, and project the
state back into h hidden dimension. At the end, dropout is also
applied.
"""
def __init__(
self,
init_method,
output_layer_init_method,
scale: int = 4,
):
super(ParallelMLP, self).__init__()
args = get_args()
# Project to 4h.
self.dense_h_to_4h = mpu.ColumnParallelLinear(
args.hidden_size,
scale * args.hidden_size,
gather_output=False,
init_method=init_method,
# skip_bias_add=True,
)
self.activation_func = fast_gelu
# Project back to h.
self.dense_4h_to_h = mpu.RowParallelLinear(
scale * args.hidden_size,
args.hidden_size,
input_is_parallel=True if args.tensor_model_parallel_size > 1 else False,
init_method=output_layer_init_method,
# skip_bias_add=True,
)
def forward(self, hidden_states):
# [s, b, 4hp]
intermediate_parallel, _ = self.dense_h_to_4h(hidden_states)
intermediate_parallel = self.activation_func(intermediate_parallel)
# [s, b, h]
output, output_bias = self.dense_4h_to_h(intermediate_parallel)
return output, output_bias
CrossEntropy
交叉熵的平行计算。核心类为_VocabParallelCrossEntropy。我们在原理篇中讲过交叉熵的并行计算,其优化核心是将通讯量从$bsv$降至$b*s$。但是Megatron代码中定义的交叉熵计算方式,稍微复杂一些,也和我们一般理解的交叉熵有些许差异。
class _VocabParallelCrossEntropy(torch.autograd.Function):
"""
分布式计算Loss
"""
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, vocab_parallel_logits, target):
# 1. logit - global max(logit)操作,主要目的是防溢出
logits_max = torch.max(vocab_parallel_logits, dim=-1)[0] # (b, s, 1)
torch.distributed.all_reduce( # (b, s, 1)
logits_max,
op=torch.distributed.ReduceOp.MAX, # 找全局最大值
group=get_tensor_model_parallel_group(),
)
# Subtract the maximum value.
vocab_parallel_logits.sub_(logits_max.unsqueeze(dim=-1)) # 原始GPU上维护的logits减去每行最大值(防止溢出)
# 2、根据当前进程id,取出当前进程所维护词表序号等信息
# 函数,能够获取当前进程所维护词表的start_index和end_index
get_vocab_range = VocabUtility.vocab_range_from_per_partition_vocab_size
# 这块GPU上logits最后一维的大小,等于所维护的词表的大小(v/N)
partition_vocab_size = vocab_parallel_logits.size()[-1]
# 取得当前进程所在TP组中的序号
rank = get_tensor_model_parallel_rank()
# 取得当前进程所在TP组的总进程数
world_size = get_tensor_model_parallel_world_size()
# 取得当前进程所维护的词表的start_index和end_index
vocab_start_index, vocab_end_index = get_vocab_range(
partition_vocab_size, rank, world_size
)
# 3. 基于真值,取出每个token在真值位置上的logit(即和真值的相似度)
# Create a mask of valid vocab ids (1 means it needs to be masked)
target_mask = (target < vocab_start_index) | (target >= vocab_end_index) # target = (b, s)
masked_target = target.clone() - vocab_start_index
masked_target[target_mask] = 0
# Get predicted-logits = logits[target].
# For Simplicity, we convert logits to a 2-D tensor with size
# [*, partition-vocab-size] and target to a 1-D tensor of size [*].
logits_2d = vocab_parallel_logits.view(-1, partition_vocab_size) # (b*s, v/N)
masked_target_1d = masked_target.view(-1) # (b*s)
arange_1d = torch.arange( # [b*s]
start=0, end=logits_2d.size()[0], device=logits_2d.device
)
# logits_2d[arange_1d, masked_target_1d]:
# tensor的切片操作。arange_1d:取出所有的行。masked_target_1d:取出logit
predicted_logits_1d = logits_2d[arange_1d, masked_target_1d] # (b*s)
predicted_logits_1d = predicted_logits_1d.clone().contiguous()
predicted_logits = predicted_logits_1d.view_as(target) # (b, s)
predicted_logits[target_mask] = 0.0
# All reduce is needed to get the chunks from other GPUs.
torch.distributed.all_reduce( # allreduce之后得到的logit矩阵为(b, s),每一个位置表示对应真值位置的预测logit
predicted_logits,
op=torch.distributed.ReduceOp.SUM,
group=get_tensor_model_parallel_group(),
)
# Sum of exponential of logits along vocab dimension across all GPUs.
exp_logits = vocab_parallel_logits # (b, s, v/N)
torch.exp(vocab_parallel_logits, out=exp_logits)
sum_exp_logits = exp_logits.sum(dim=-1) # (b, s)
torch.distributed.all_reduce(
sum_exp_logits,
op=torch.distributed.ReduceOp.SUM,
group=get_tensor_model_parallel_group(),
)
# 4. 计算Loss = log(sum(exp(logits))) - predicted-logit.
loss = torch.log(sum_exp_logits) - predicted_logits # (b, s)
# Store softmax, target-mask and masked-target for backward pass.
exp_logits.div_(sum_exp_logits.unsqueeze(dim=-1))
ctx.save_for_backward(exp_logits, target_mask, masked_target_1d)
return loss
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
# Retreive tensors from the forward path.
softmax, target_mask, masked_target_1d = ctx.saved_tensors
# All the inputs have softmax as their gradient.
grad_input = softmax
# For simplicity, work with the 2D gradient.
partition_vocab_size = softmax.size()[-1]
grad_2d = grad_input.view(-1, partition_vocab_size)
# Add the gradient from matching classes.
arange_1d = torch.arange(start=0, end=grad_2d.size()[0], device=grad_2d.device)
grad_2d[arange_1d, masked_target_1d] -= 1.0 - target_mask.view(-1).float()
# Finally elementwise multiplication with the output gradients.
grad_input.mul_(grad_output.unsqueeze(dim=-1))
return grad_input, None